728x90
반응형
1. 그래프(Graph)란 무엇일까
- 정점과 간선으로 이루어진 자료구조이다. 즉, 연결된 정점간의 관계를 표현할 수 있다.
- Cyclic 하다. -> 순환할 수 있다.
- 그래프의 용도 : 지하철 노선도, 통신 네트워크 등 ...
(1) 그래프 구조 및 특징
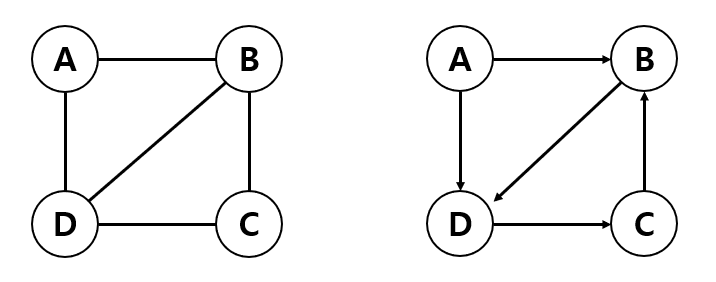
- 정점(Vertex) : 각 노드
- 간선(Edge) : 노드와 노드를 연결하는 선 ( = link, branch)
- 인접 정점(Adjacent vertex) : 간선 하나를 두고 바로 연결된 정점
- 정점의 차수(Degree) : 무방향 그래프에서 하나의 정점에 인접한 정점의 수
- 무방향 그래프의 모든 정점 차수의 합 = 그래프 간선의 수 * 2
- 진입 차수 (In - degree) : 방향 그래프에서 외부에서 오는 간선의 수
- 진출 차수 (Out - degree) : 방향 그래프에서 외부로 나가는 간선의 수
- 경로 길이 (Path length) : 경로를 구성하는데 사용된 간선의 수
- 단순 경로 (Simple path) : 경로 중에서 반복되는 정점이 없는 경우
- 사이클 (Cycle) : 단순 경로의 시작 정점과 끝 정점이 동일한 경우
(2) 그래프 종류
무방향 그래프
- 간선에 방향이 없는 그래프 ( 양방향으로 이동이 가능하다.)
- 정점 A-B 간선의 표현 : (A,B) = (B,A)
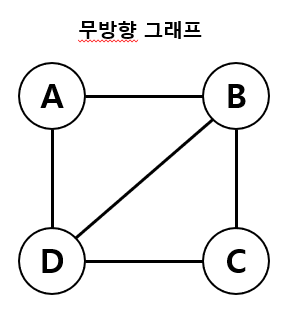
무방향 그래프
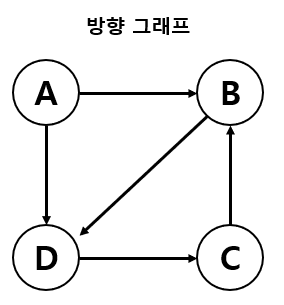
- 간선에 방향이 있는 그래프 ( 해당 방향으로만 이동이 가능하다.)
- 정점 A -> B 간선의 표현 : <A,B> ≠ <B,A>
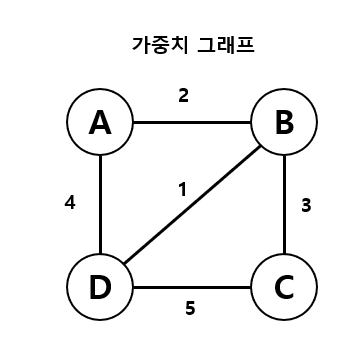
가중치 그래프
- 간선에 값이 있는 그래프 (이동 비용이 존재한다.)
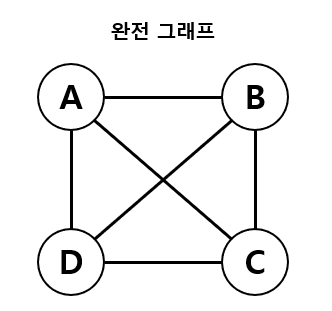
완전 그래프
- 모든 정점이 서로 연결되어 있는 그래프
- 정점이 N개일 경우, 간선의 수는 n(n-1) / 2 개
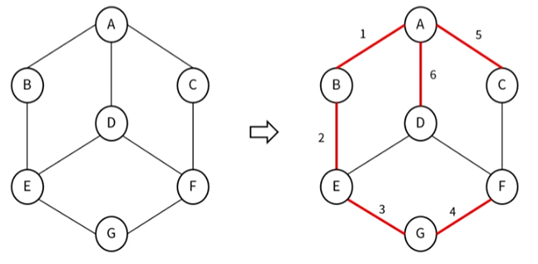
2. 그래프 탐색
(1) DFS (Depth-First Search)
- 깊이 우선 탐색
- 각 노드에 방문했는지 여부를 체크할 배열과 스택을 이용하여 구현
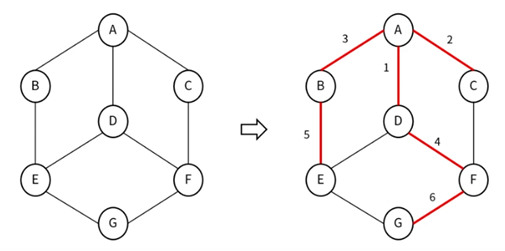
(2) BFS (Breath-First Search)
- 너비 우선 탐색
- 각 노드에 방문했는지 여부를 체크할 배열과 큐를 이용하여 구현
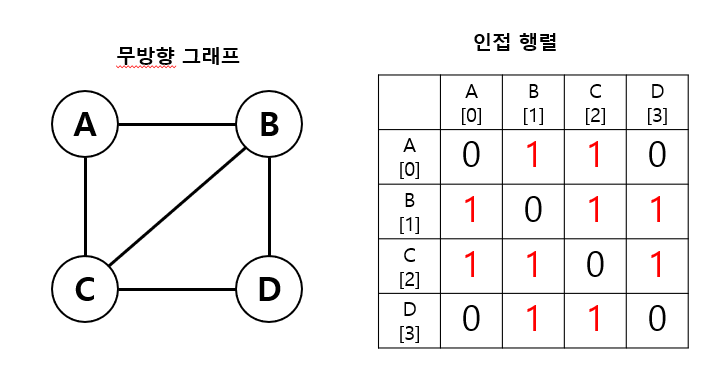
3. 그래프 구현
(1) 인접 행렬 (Adjacency Matrix)
- 2차원 배열을 이용한다.
- 장점 : 간선 정보의 확인과 업데이트가 빠르다. (시간 복잡도 : O(1))
- 단점 : 인접 행렬을 위한 메모리 공간이 필요하다. (필요 공간 : 정점 개수 * 정점 개수)
인접 행렬 그래프 코드로 구현하기
class MyGraphMatrix {
char[] vertices;
int[][] adjMat;
int elemCnt;
public MyGraphMatrix() {}
public MyGraphMatrix(int size) {
this.vertices = new char[size];
this.adjMat = new int[size][size];
this.elemCnt = 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.elemCnt == this.vertices.length;
}
public void addVertex(char data) {
if (this.isFull()) {
System.out.println("Graph is Full!");
return;
}
this.vertices[this.elemCnt++] = data;
}
public void addEdge(int x, int y) { // 무방향 그래프일 때
this.adjMat[x][y] = 1;
this.adjMat[y][x] = 1;
}
public void addDirectedEdge(int x, int y) { // 방향 그래프일 때
this.adjMat[x][y] = 1;
}
public deleteEdge(int x, int y) {
this.adjMat[x][y] = 0;
this.adjMat[y][x] = 0;
}
public deleteDirectedEdge(int x, int y) {
this.adjMat[x][y] = 0;
}
public void printAdjacentMatrix() {
System.out.println(" ");
for(char item : this.vertices) {
System.out.print(item + " ");
}
System.out.println();
for (int i =0;i < this.elemCnt; i++) {
System.out.print(this.vertices[i] + " ");
for (int j = 0; j <this.elemCnt; j++) {
System.out.print(this.adjMat[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
인접 행렬 그래프의 DFS, BFS
class MyGraphMatrix2 extends MyGraphMatrix {
public MyGraphMatrix2(int size) {
super(size);
}
public void dfs(int id) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[this.elemCnt];
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(id);
visited[id] = true;
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
int curId = stack.pop();
System.out.print(this.vertices[curId] + " ");
for (int i = this.elemCnt-1 ; i>=0 ; i--) {
if (this.adjMat[curId][i] == 1 && visited[i] == false) {
stack.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public void bfs(int id) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[this.elemCnt];
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(id);
visited[id] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int curId = queue.poll();
System.out.println(this.vertices[curid] + " ");
for (int i = this.elemCnt -1 ; i>=0 ; i--) {
if (this.adjMat[curId][i] == 1 && visited[i] == false) {
queue.offer(i);
visited[i] = true;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
(2) 인접 리스트 (Adjacency List)
- 연결 리스트를 이용한다.
- 장점 : 메모리 사용량이 상대적으로 적고, 노드의 추가 · 삭제가 빠르다.
- 단점 : 간선 정보 확인이 상대적으로 오래 걸린다.
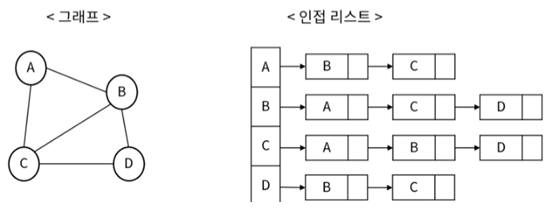
인접 리스트 그래프 코드로 구현하기
class Node {
int id;
Node next;
public Node(int id, Node next) {
this.id = id;
this.next = next;
}
}
class MyGraphList {
char[] vertices;
Node[] adjList;
int elemCnt;
public MyGraphList() {}
public MyGraphList(int size) {
this.vertices = new char[size];
this.adjList = new Node[size];
this.elemCnt = 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.elemCnt == this.vertices.length;
}
public void addVertex(char data) {
if (this.isFull()) {
System.out.println("Graph is Full");
return;
}
this.vertices[this.elemCnt++] = data;
}
public void addEdge(int x, int y) { // 무방향일 때
this.adjList[x] = new Node(y,this.adjList[x]);
this.adjList[y] = new Node(x,this.adjList[y]);
}
public void addDirectedEdge(int x, int y) { // 방향일 때
this.adjList[x] = new Node(y,this.adjList[x]);
}
public void printAdjacentList() {
for (int i =0; i< this.elemCnt; i++) {
System.out.print(this.vertices[i] + " : ");
Node cur = this.adjList[i];
while(cur != null) {
System.out.print(this.vertices[cur.id] + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
인접 리스트 그래프의 DFS, BFS
class MyGraphList2 extends MyGraphList {
public MyGraphList2(int size) {
super(size);
}
public void dfs(int id) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[this.elemCnt];
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(id);
visited[id] = true;
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
int curId = stack.pop();
System.out.print(this.vertices[curId] + " ");
Node cur = this.adjList[curId];
while( cur != null) {
if (visited[cur.id] == false) {
stack.push(cur.id);
visited[cur.id] = true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public void bfs(int id) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[this.elemCnt];
Queue<Integer> queue= new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(id);
visited[id] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int curId = queue.poll();
System.out.print(this.vertices[curId] + " ");
Node cur = this.adjList[curId];
while(cur != null) {
if (visited[cur.id] == false) {
queue.add(cur.id);
visited[cur.id] = true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}반응형
'Knowledge > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 구간합 (1) | 2024.06.14 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] 비선형 자료구조 - 트라이 (1) | 2023.11.30 |
| [자료구조] 비선형 자료구조 - 이진 탐색 트리 (0) | 2023.11.28 |
| [자료구조] 비선형 자료구조 - 트리 (0) | 2023.11.27 |
| [자료구조] 트리와 그래프의 차이 (0) | 2023.11.27 |